LASER CUTTING INDUSTRY
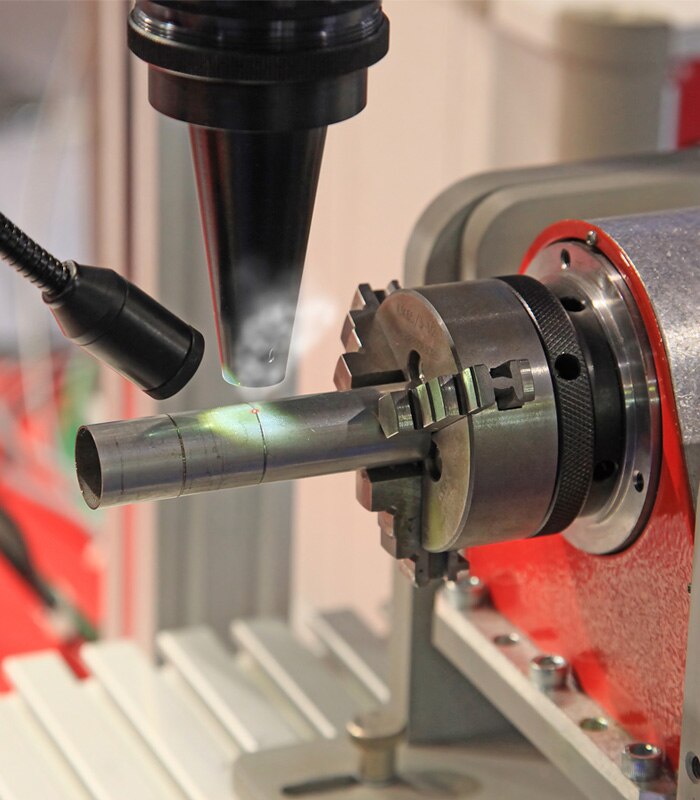
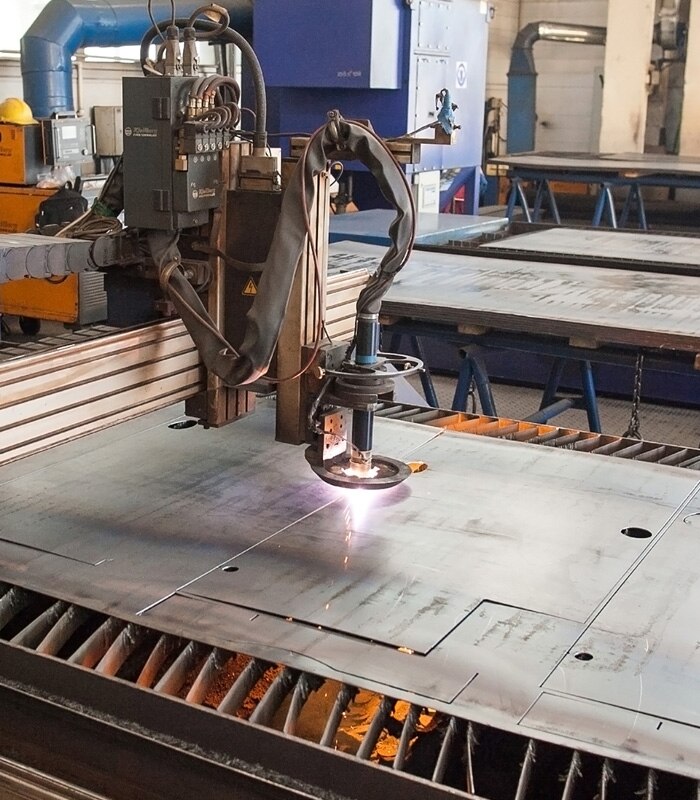
Lasers have become a universal tool in many manufacturing sectors. Lasers are routinely used when processing metals and other materials. Lasers are widely used for the following purposes: cutting, welding, soldering, surface treatment, marking, micromachining, pulsed laser deposition, lithography & alignment.
The global laser cutting machine market is expected to reach $5.7 billion by 2022, growing at a CAGR of 9.3% between 2016 to 2022.
Some of the key manufacturers of laser cutting machines include:
- Rofin-Sinar
- Trumpf
- Amada
- Bystronic
- Mazak
Laser processing methods offer many advantages over traditional mechanical approaches. These include:
- High precision and accuracy when manipulating a range of materials
- High quality finish with clean cutting surfaces
- Fabrication of small and fine structures
- Avoidance of mechanical stress caused by drills and blades
- Higher processing speed with increased throughput
- Process material can be cut without handling
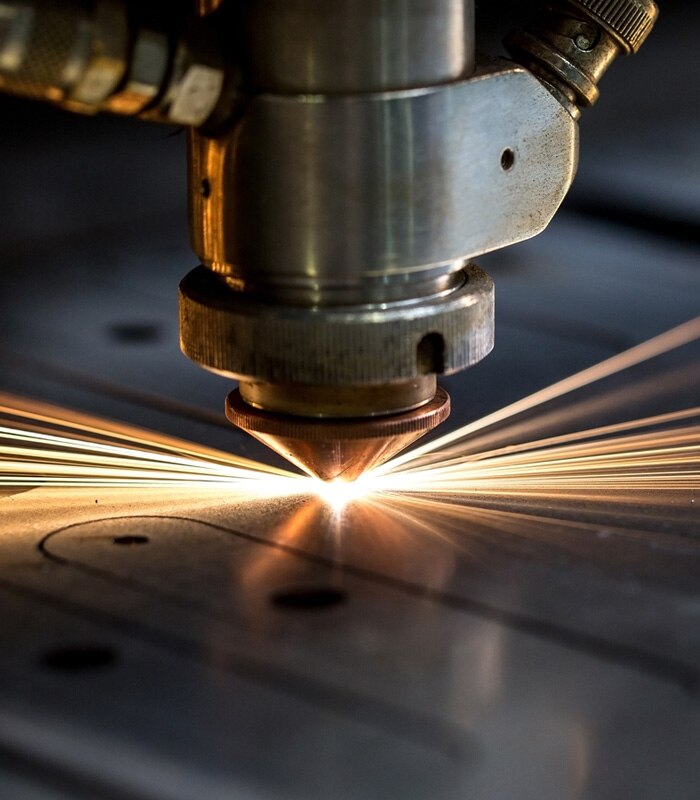
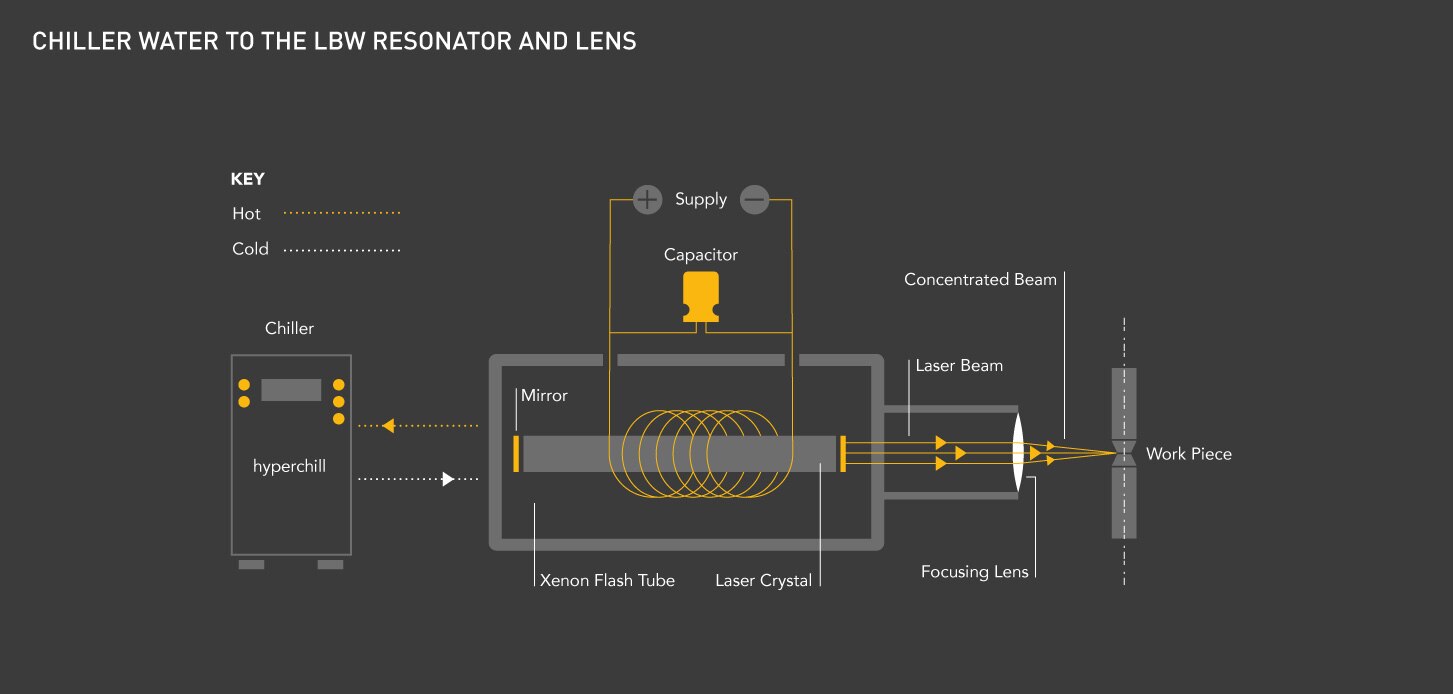
Laser techniques generally employ high optical intensities to a concentrated area on the processing material. The high energy levels result in intense heat (possibly evaporation) and plasma generation. The intense energy levels can be controlled to manipulate the process material resulting in cutting, etching, marking etc. The high spatial coherence of laser light can be precisely focused or pulsed to achieve accuracy when processing the target material.
Chillers play an essential role in laser applications. To ensure the laser operates reliably, several components must be cooled in the system. Failure to remove sufficient heat can diminish the accuracy of the cut and deform parts of the laser. In time this would also result in costly down-time and increased laser machine maintenance costs.